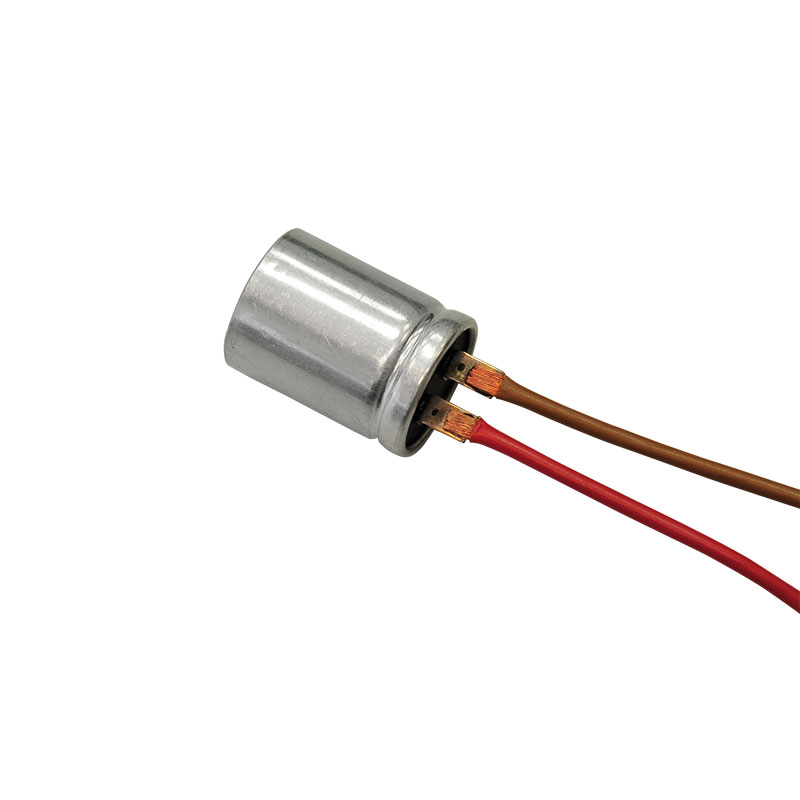
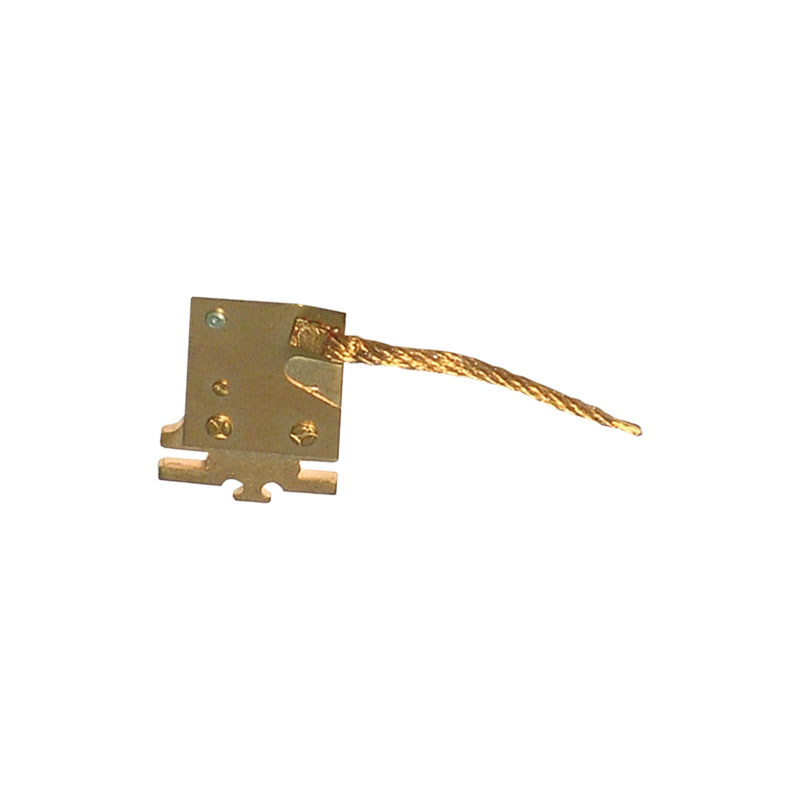
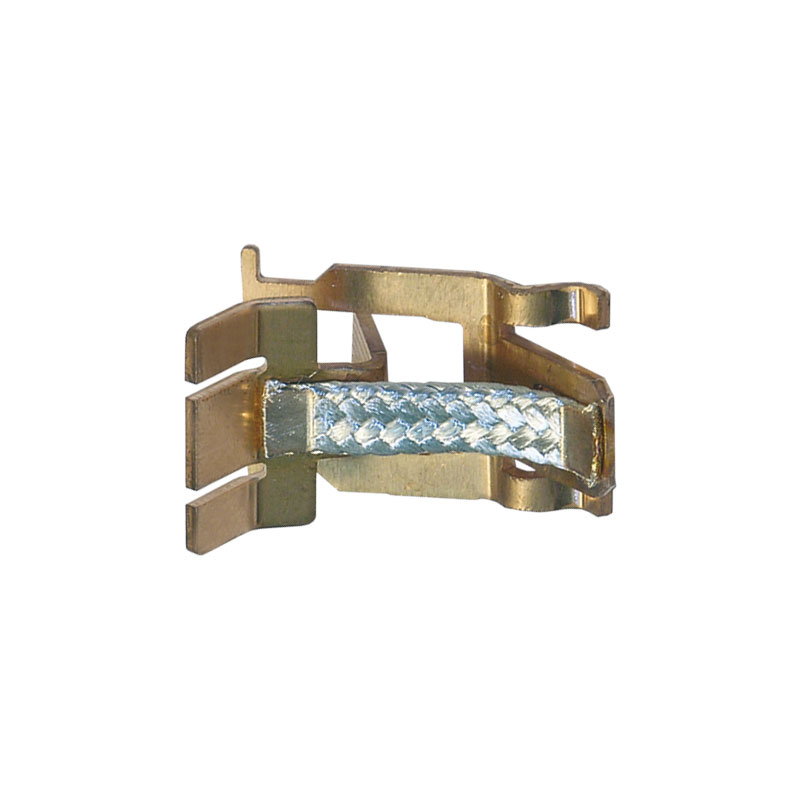
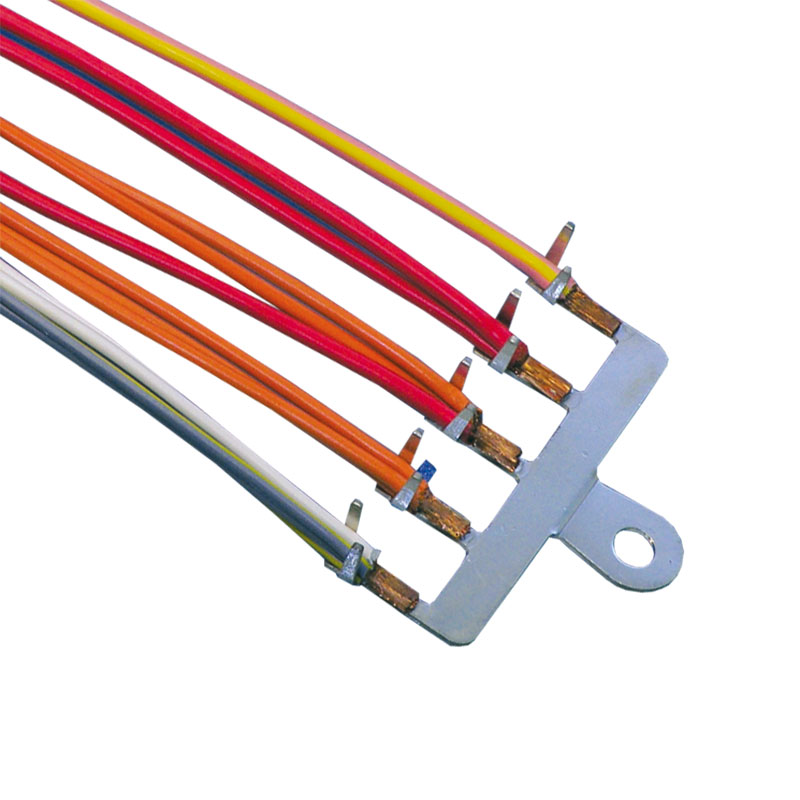
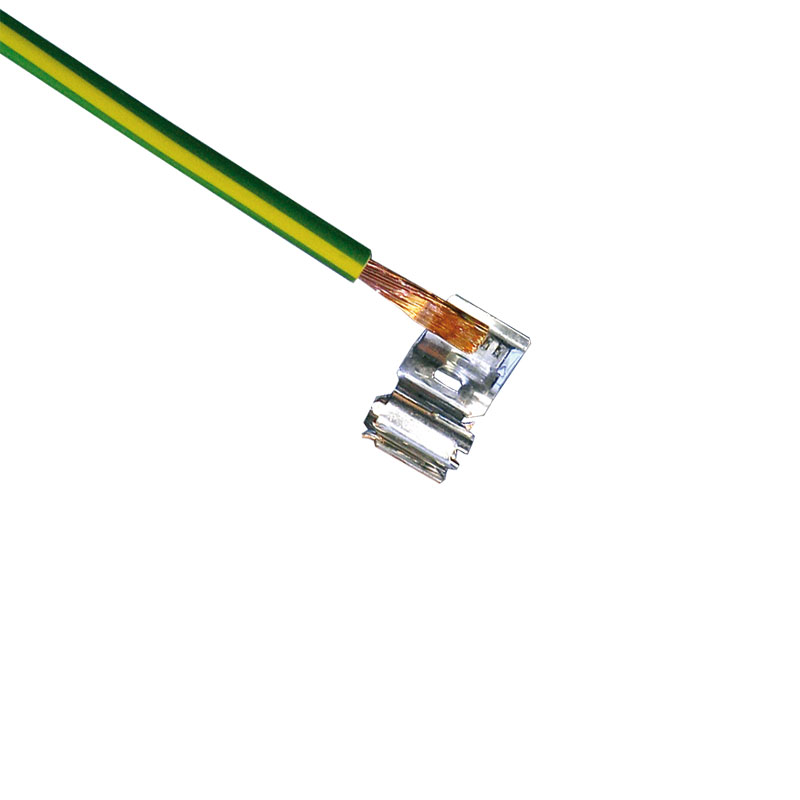
Terminal welding
our know-how for stable strand-terminal connectionsTerminal welding – high-quality connections with the lowest transition resistance possible
Terminal welding by means of resistance technology allows for connecting cable or braid strands to components such as terminals, plugs, welding rings and switches. Resistance welding can be used to process stranded wires with a cross-section of 0.1 mm² (micro range) up to 300 mm². Mixed connections and special alloys can also be joined together.
Resistance welding of stranded wires to terminals offers several advantages. On the one hand, the connections stand out due to their high mechanical strength (pull and peel force) and transition resistances that tend towards zero. On the other hand, they show no signs of aging and are not susceptible to dirt, drawing oil or oxidation. This also means that there are no abnormalities in terms of:
- mechanical load,
- electrical load,
- dynamic stress and
- environmental influences such as temperature changes, dry and wet heat or salt spray.
Aging tests, degradation checks or vibration tests show no negative effects on the connection. This is made possible by a material-to-material and “real” welded joint in the hot phase.
Another advantage of resistance welding is the ability to weld to both sides of a terminal or other connection surfaces, even at very short distances (e. g. 20 mm or less). The terminals may be tin-plated and mixed connections (metal-to-metal) can also be established.
In terminal welding, important parameters such as installation space, contact part geometries, alloys and surface coatings must already be coordinated during planning and development. We therefore recommend that you make use of STRUNK Consulting to ensure reliable terminal connections.
Three methods of terminal welding
1. By adapting the width of the terminal to the strand cross-section, it is possible to weld a cable onto the terminal directly without prior compacting.
2. The direct welding of uncompacted cables can also be implemented with a special tool. You will receive further information on this as part of the consulting.
3. The third method involves a pre-process for compacting the strand before it is welded onto the terminal. This procedure is often used in automatic machines (e. g. transfer systems) or when direct welding is impossible due to spatial restrictions of the terminal (e. g. in housing).
All methods can also be mapped under braze.
Like the processed strands, the terminal connections can also vary in cross-section. For this purpose, the initial or customer samples must first be tested for technical feasibility in our in-house laboratory (prototype development). In this process, we already gain initial insights for industrialization.
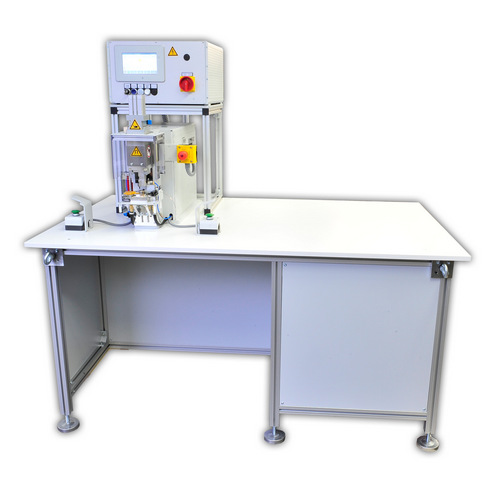
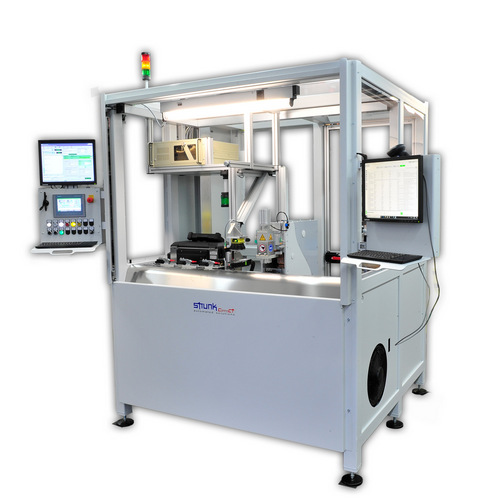
As soon as the application is classified as technically feasible and reliable, we will work out a proposal for industrialization based on your quantities and your production process. You can choose between a manual workstation, a semi-automatic version and a fully automatic system with upstream and downstream processes. Depending on this, we build for you:
- welding modules equipped with tools adapted to manual tasks,
- machines in cell design with automated processes and manual feeding or
- interlinked production lines as a transfer, rotary indexing table or tool carrier system.
Automated welding and feeding of terminals to wire processing centers using special modules is also possible.
STRUNK Connect – Your partner for terminal welding in various industries
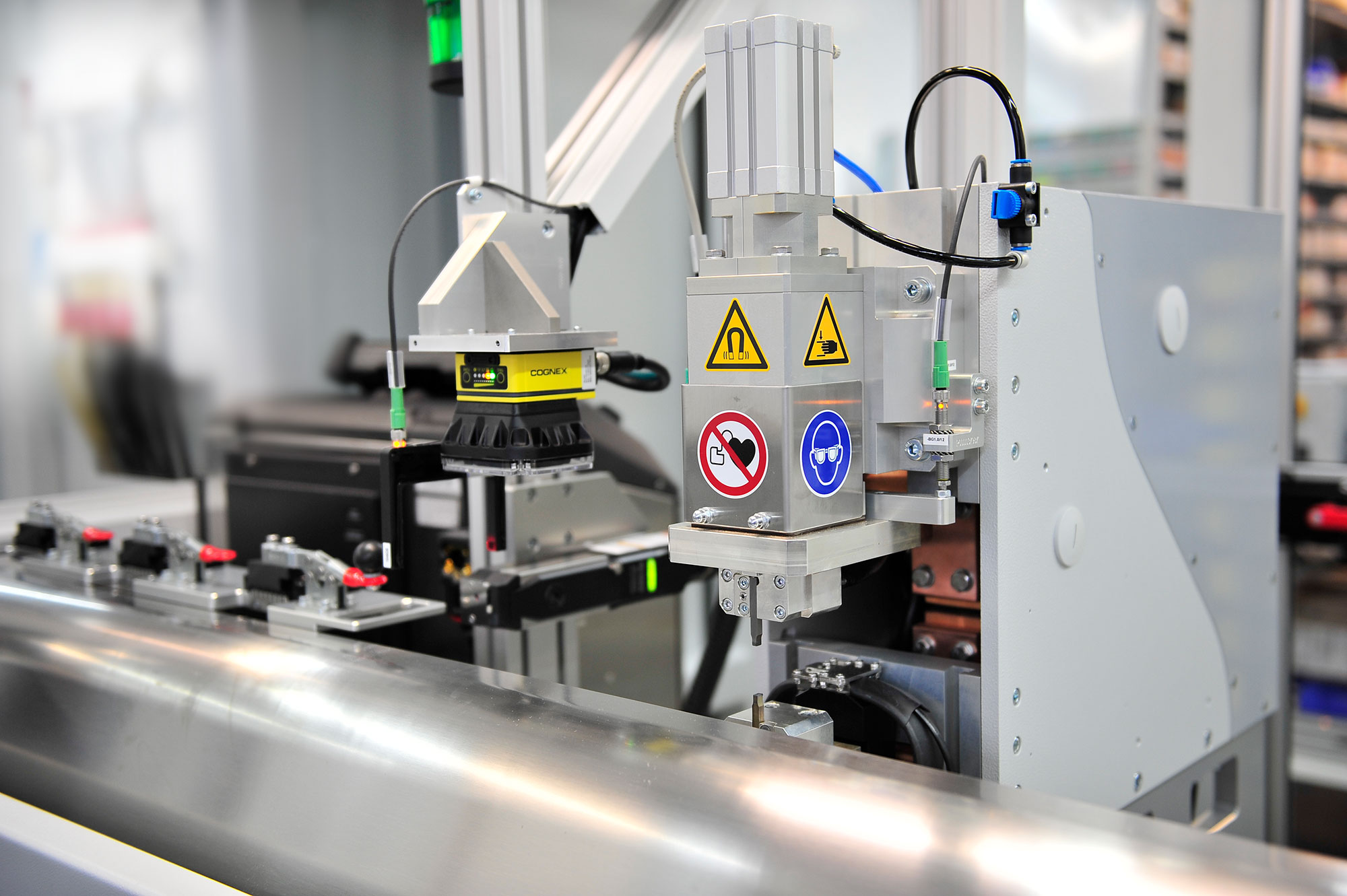
To enable you to create reliable connections from strands and components to end connectors, we adapt the necessary tools precisely to your applications or redesign them if necessary. Thus, we ensure the required positioning of the individual elements. We also achieve a consistent energy density per square millimeter this way.
Depending on the geometric shape of the components and the contacting surfaces, it is either possible to weld on the strands pre-compacted or to create the connection in a single step. With the second option, compacting and welding are carried out simultaneously in one process step. For this purpose, the geometric shape of the component’s connection surface must precisely match the strand cross-section.
With our terminal welding systems, we guarantee maximum efficiency and quality as well as optimum handling during the production process. Whether you are looking for a manual workstation for manual production, a mobile device for sequential production on the cable board or modules for integration into existing machines or lines – you have come to the right place. We also offer you semi-automatic cells and fully automatic production lines for terminal welding. These cover an almost infinite range of applications in industries such as automotive, medical technology, solar, photovoltaics, electrical appliances and defense.
By combining our intelligent power sources with application-specific tools, it is also possible to weld mixed joints and special alloys. Our team will be happy to check the technical feasibility of your application in the laboratory and create initial samples for you. Get in touch with us today!
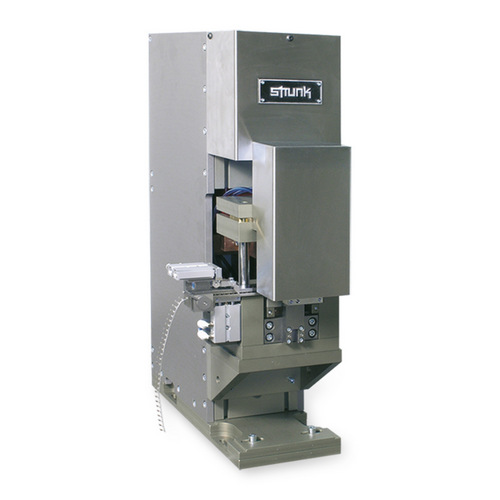
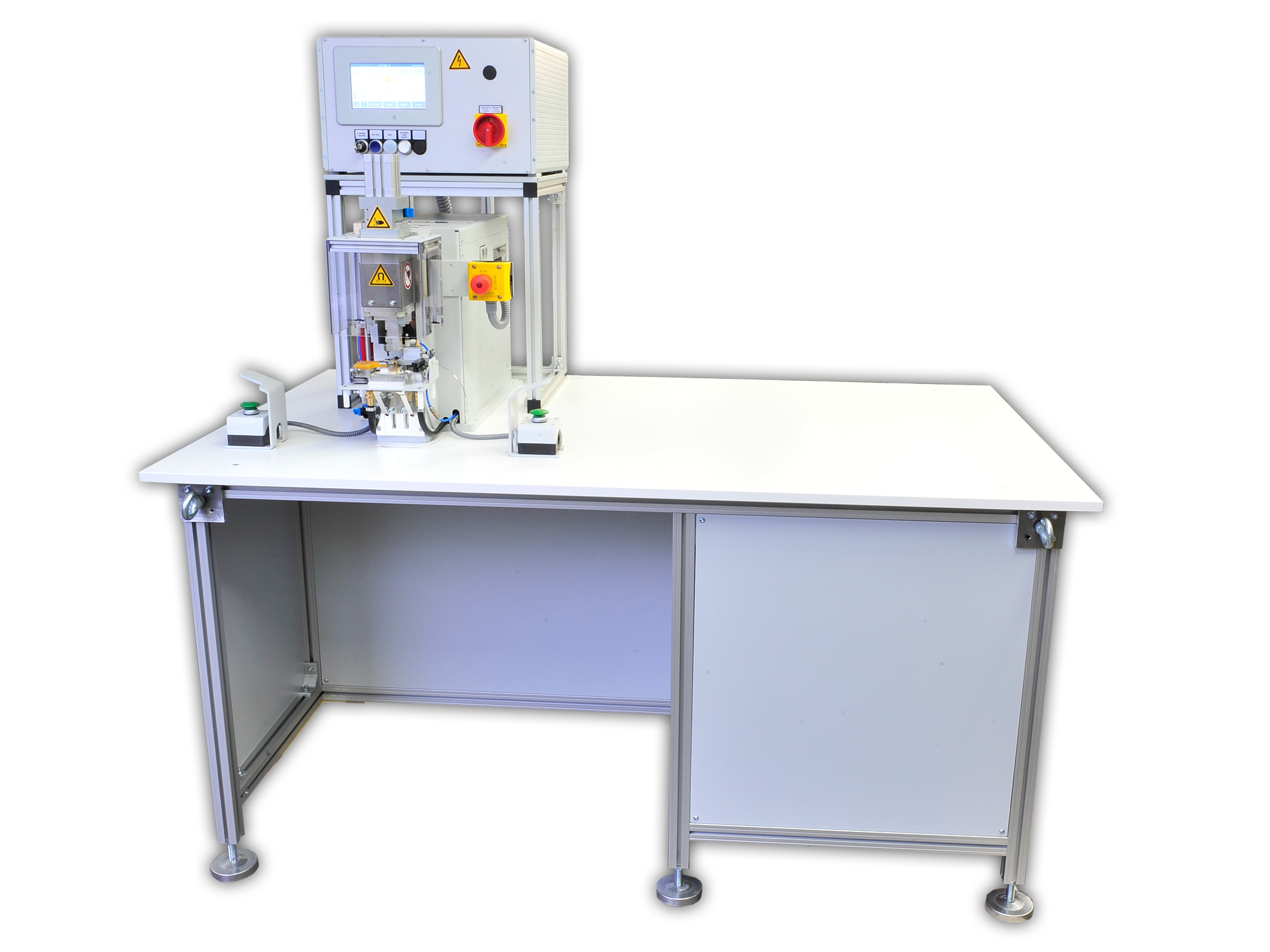
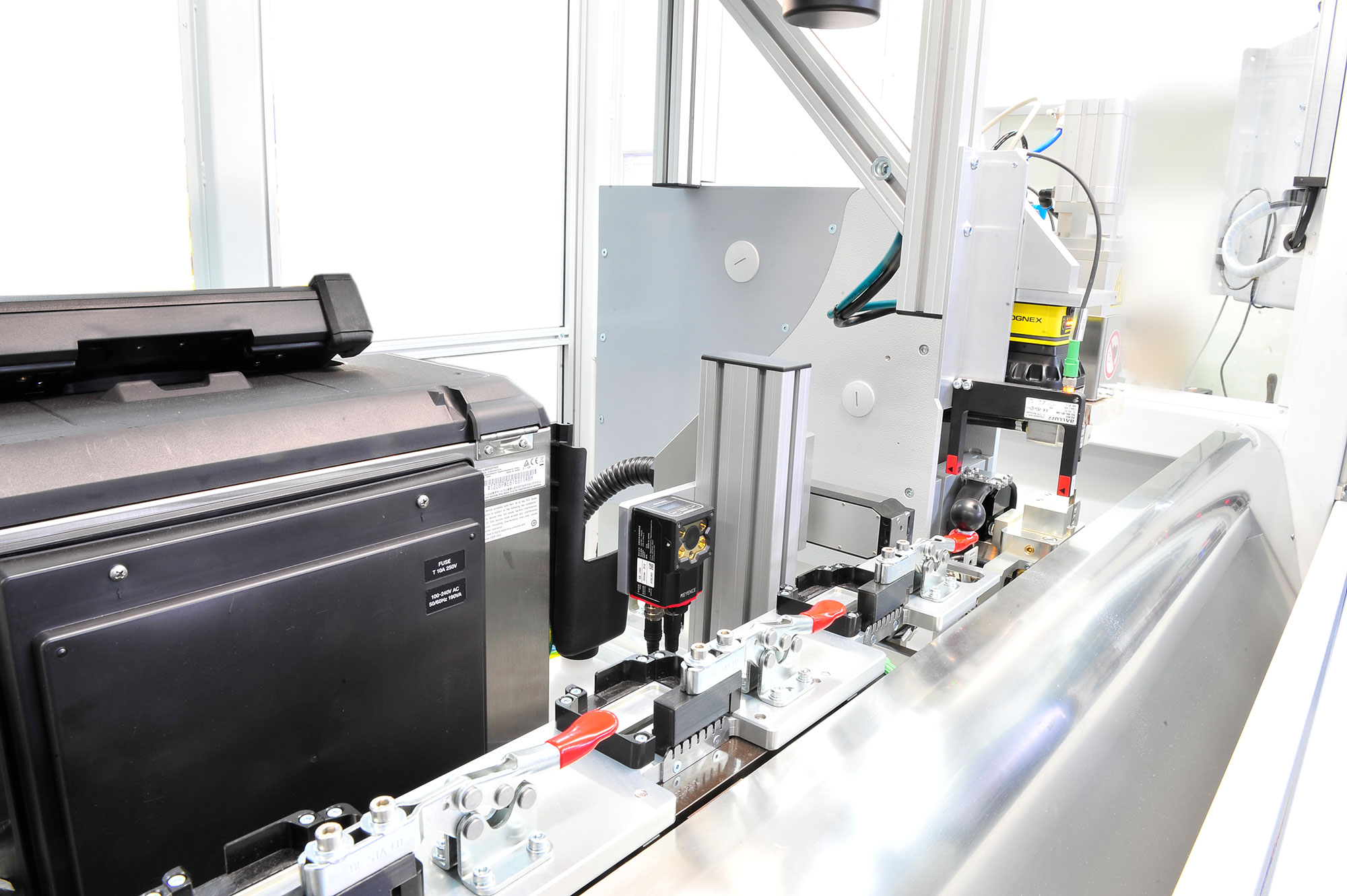
machines
(customer-specific solutions as an example)
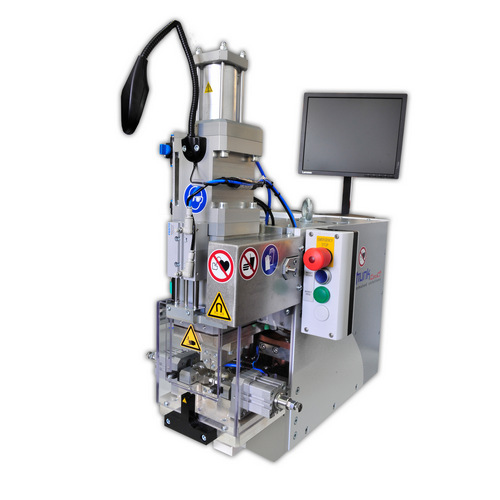
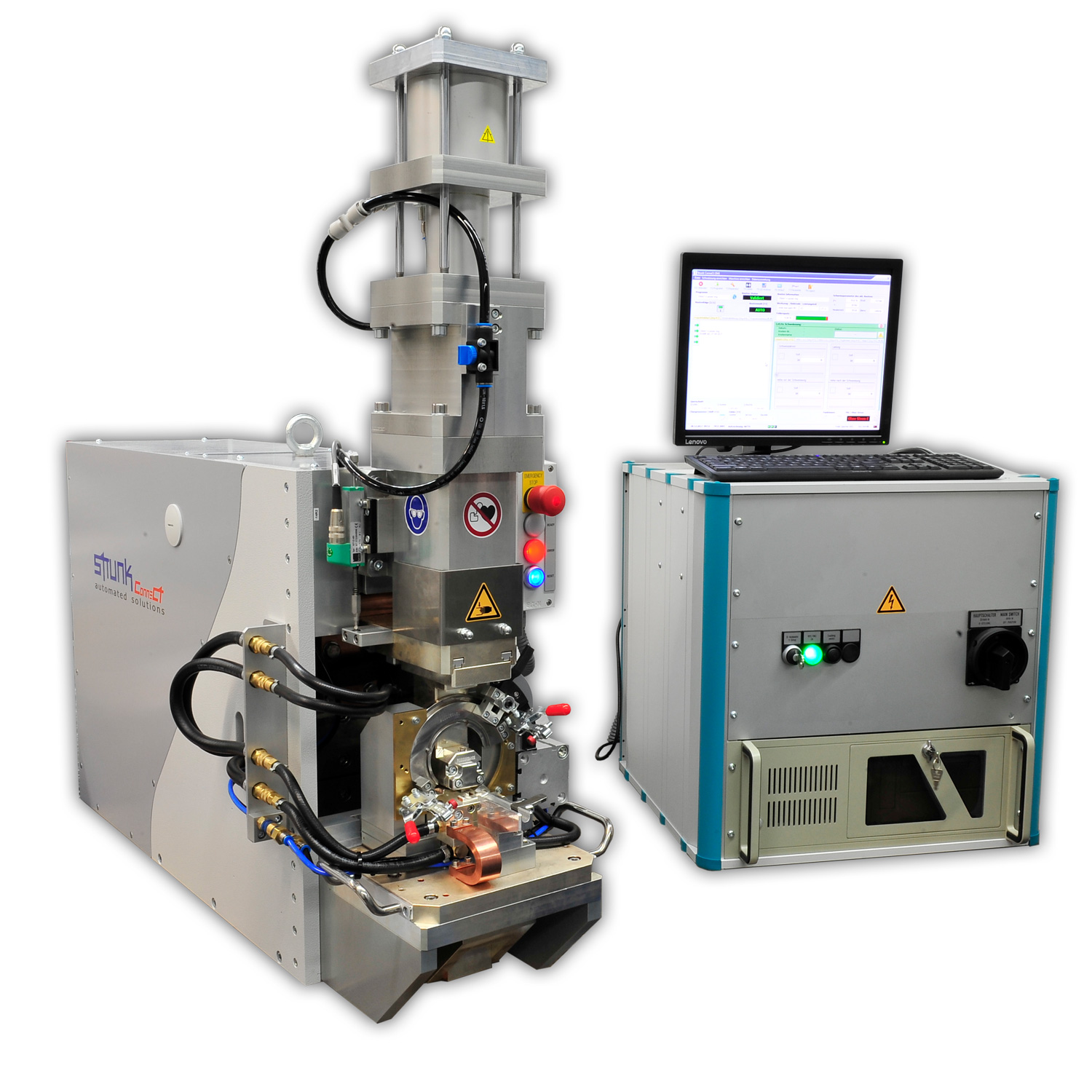
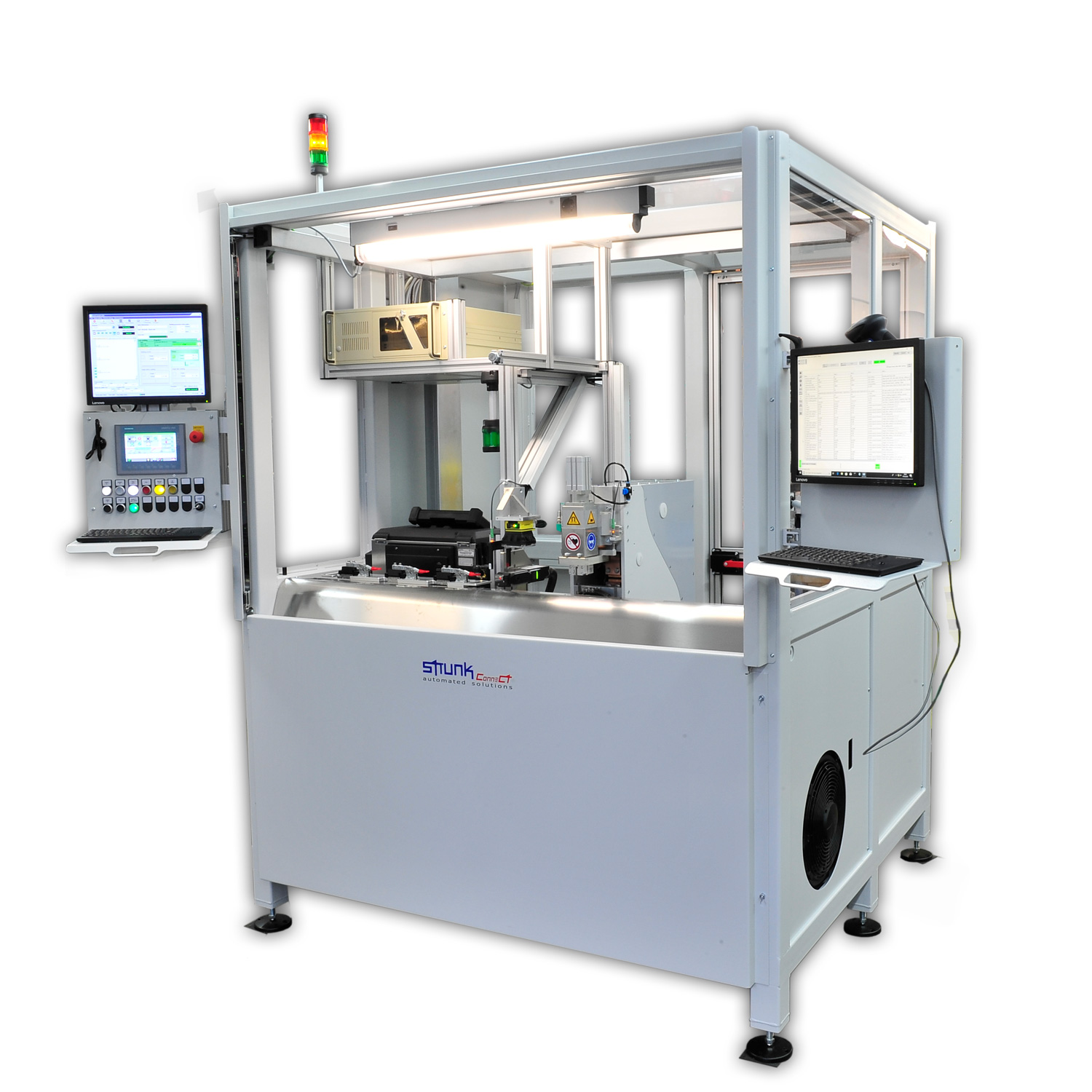
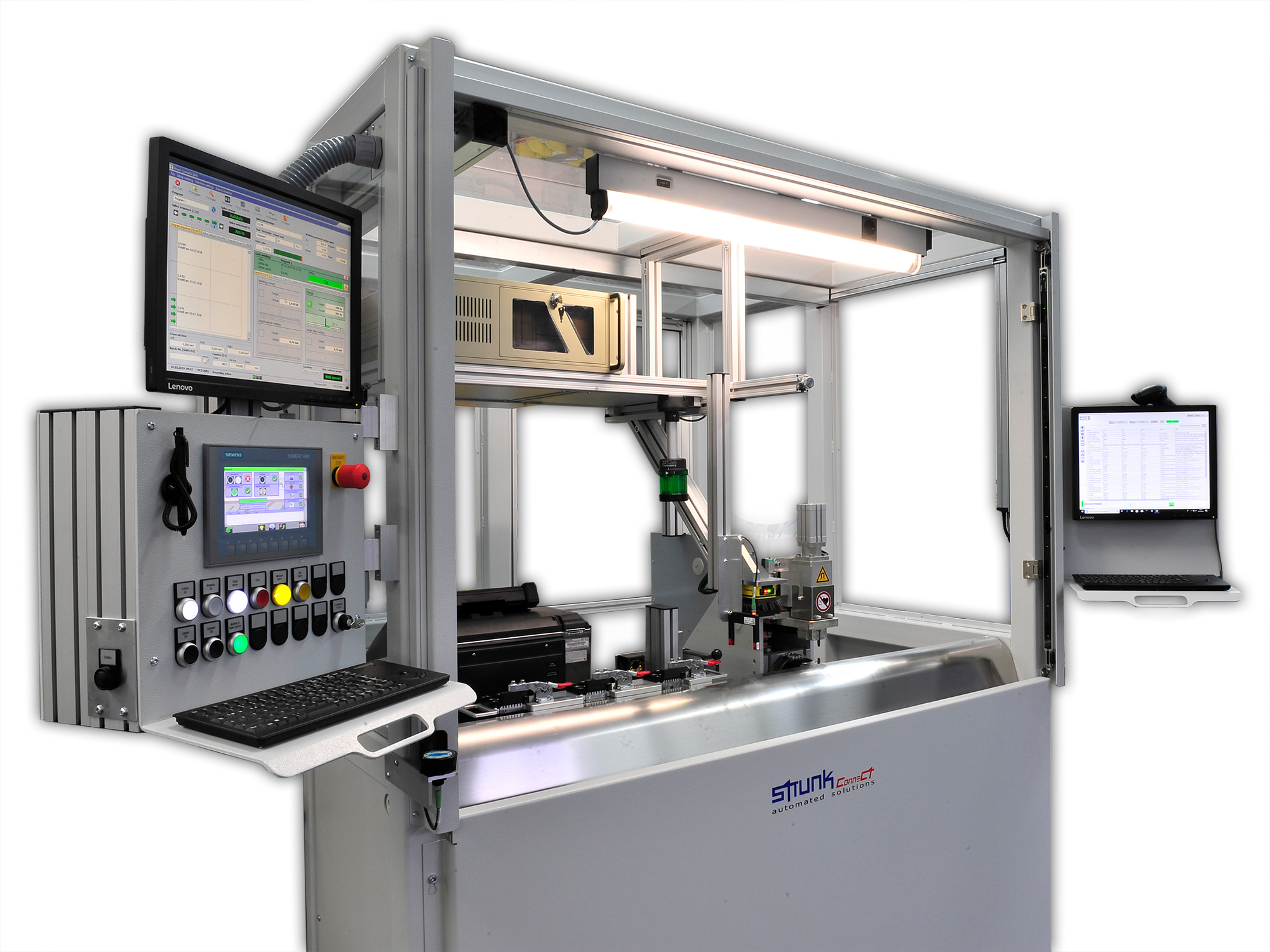
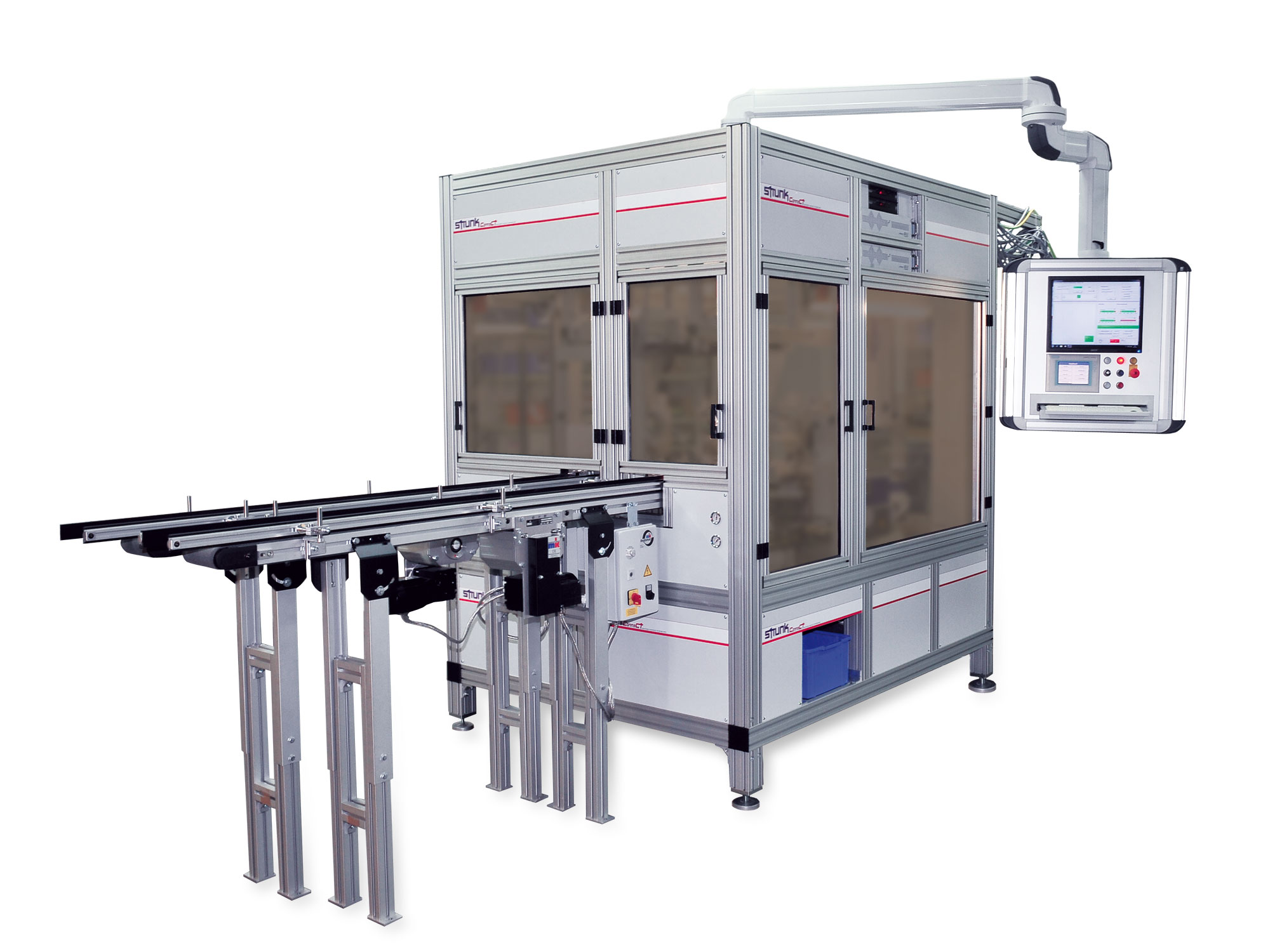
S-MMD1 with double welding tool for connecting high-temperature cables to terminals
This S-MMD1 system is equipped with a double welding tool for welding pre-crimped terminals in order to keep the position and orientation of the cable and the components stable. The tap lengths can be kept short, for example for applications with short stripping where single wire processing is difficult or impossible. It also features interfaces to crimping presses for successive work sequences.
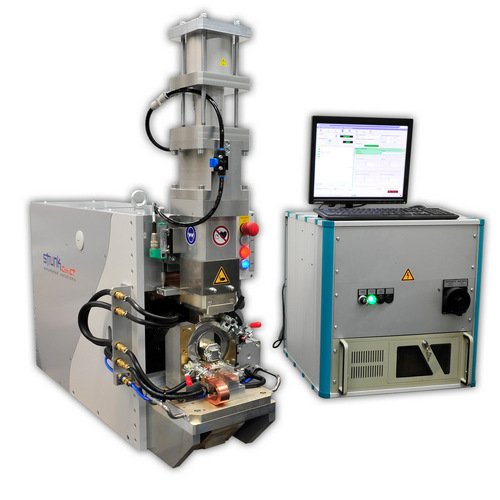
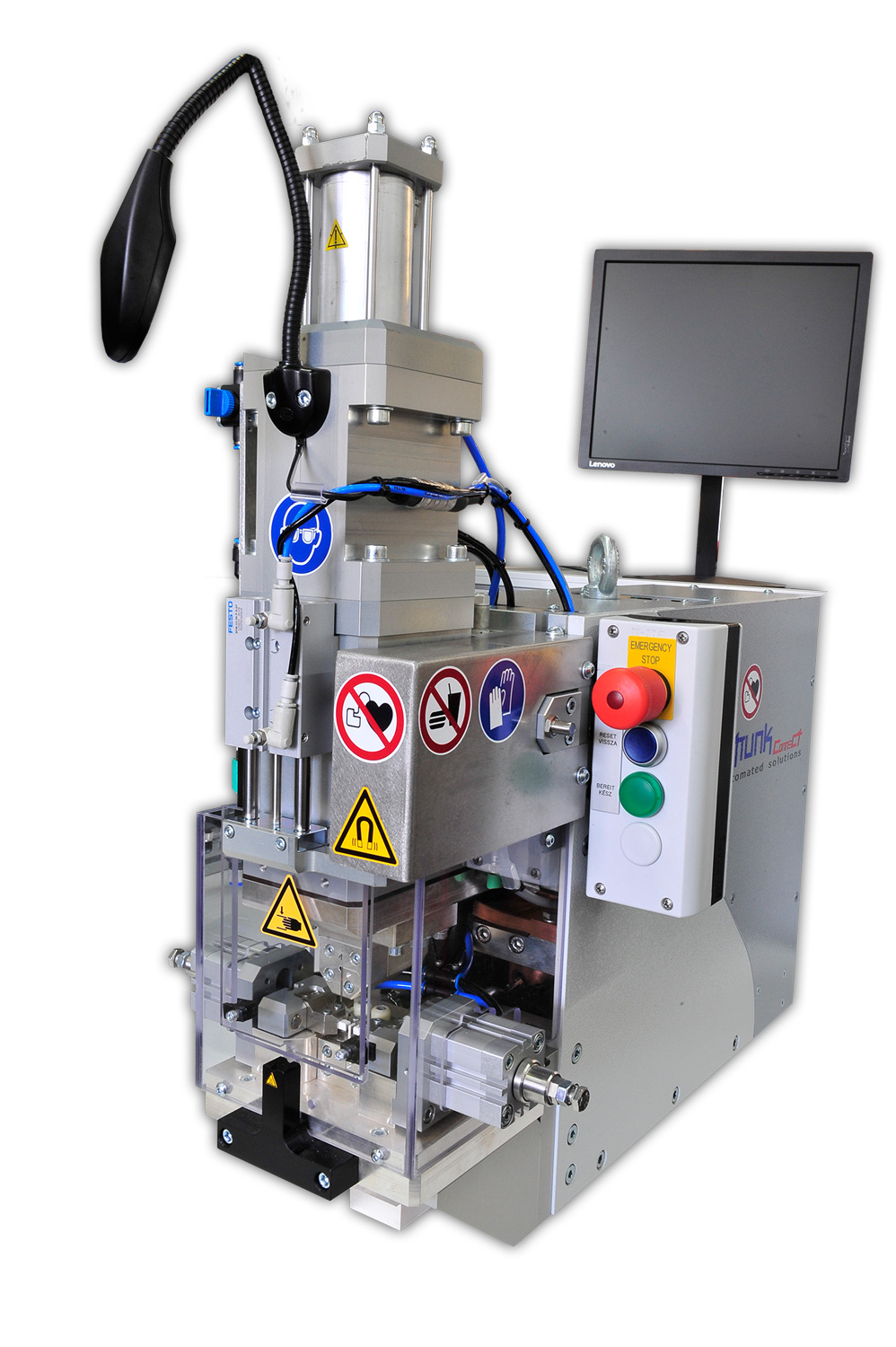
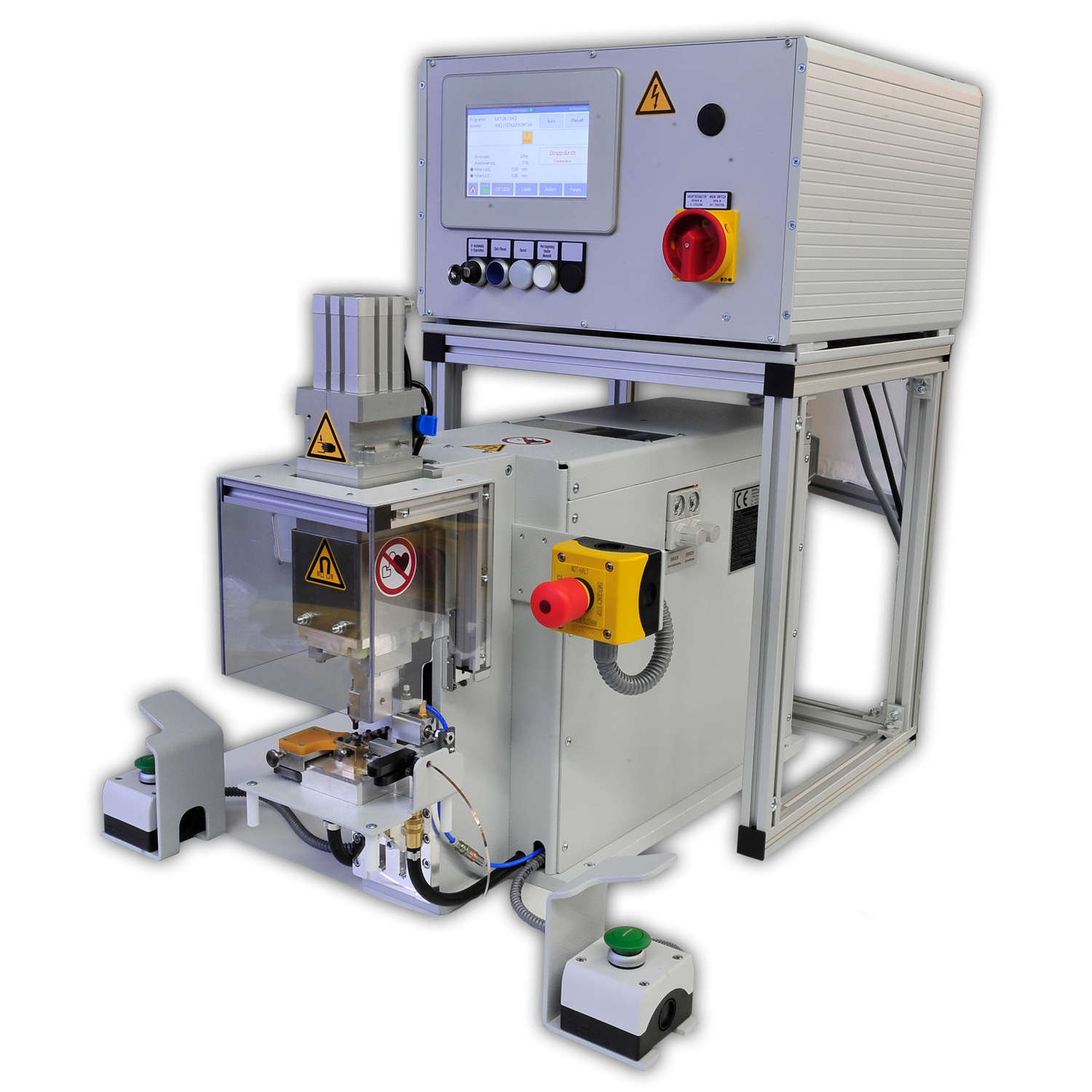
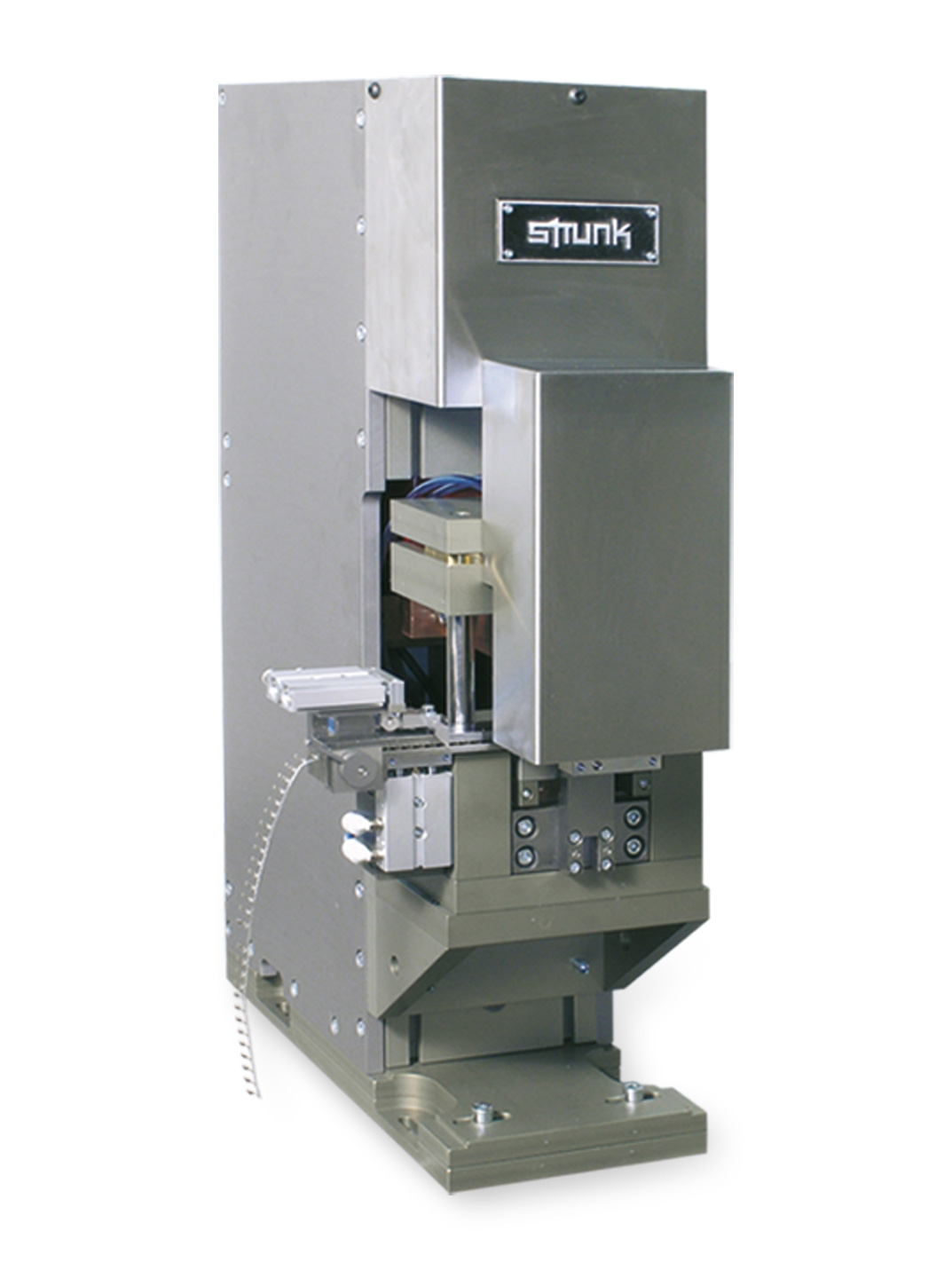
Micro welding head (MSK) for connecting braids to switch terminals under braze
This micro welding machine features a customer-specific exchangeable tool, a manual braze feed as well as an automatic braze separator. Its setup can be adjusted to your specifications and the available space in your production area.
Samples
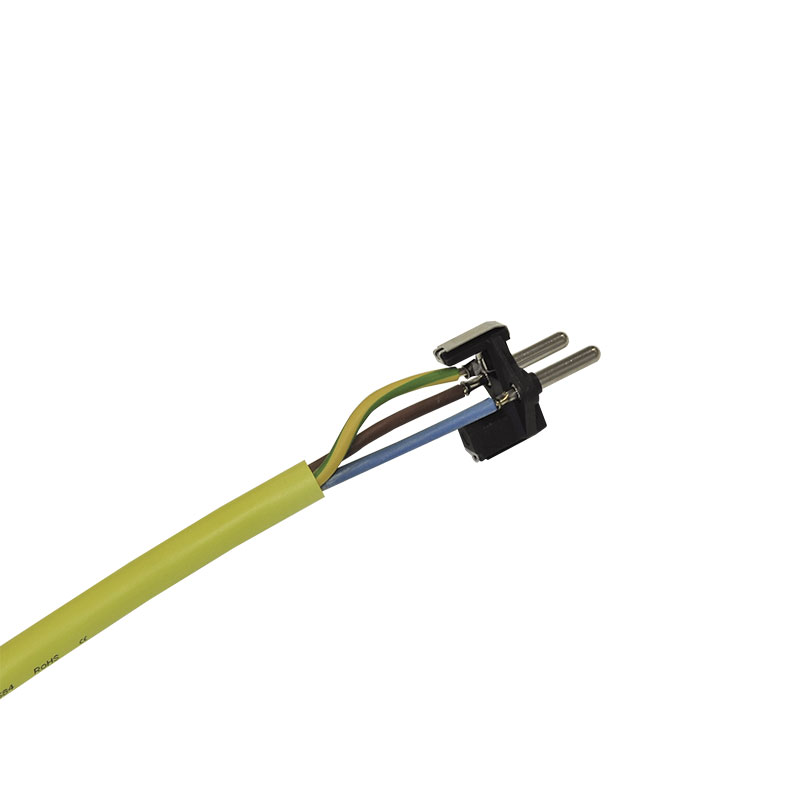
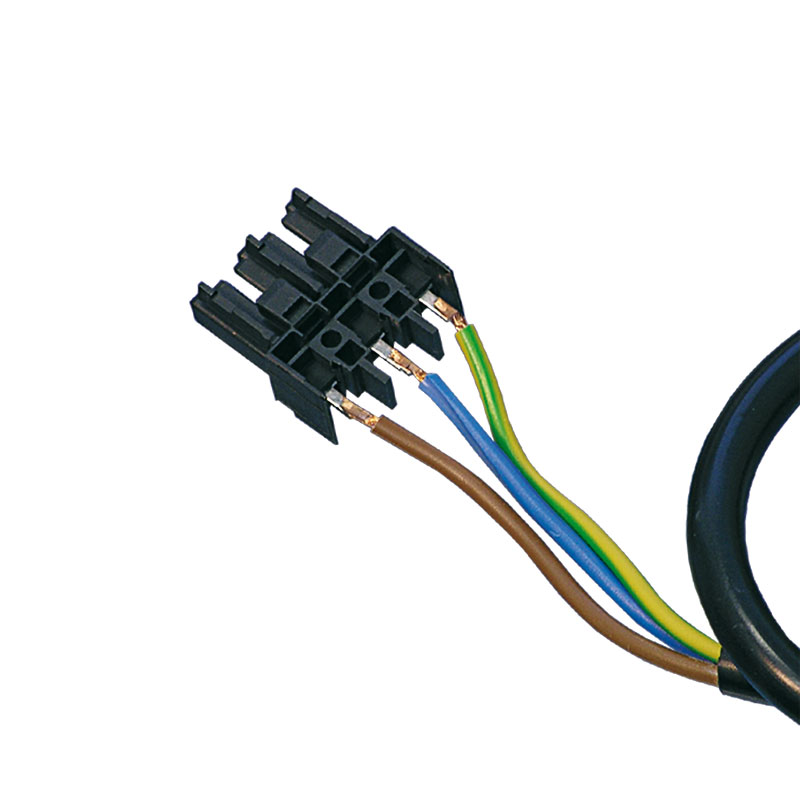
Three-wire sheathed cable to terminal, tin-plated
Flat ribbon to plug, created with a beam welding system
Slip ring
Our systems can be used to weld connections between compacted cables and slip rings without damaging the contact surfaces.
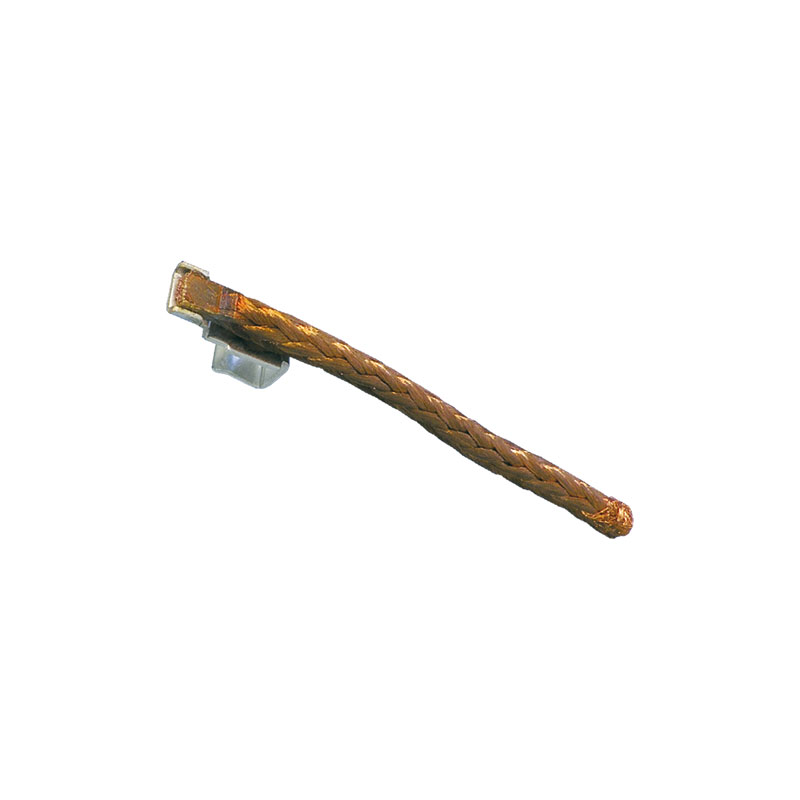
Copper braid, tin-plated, to copper terminal, tin-plated
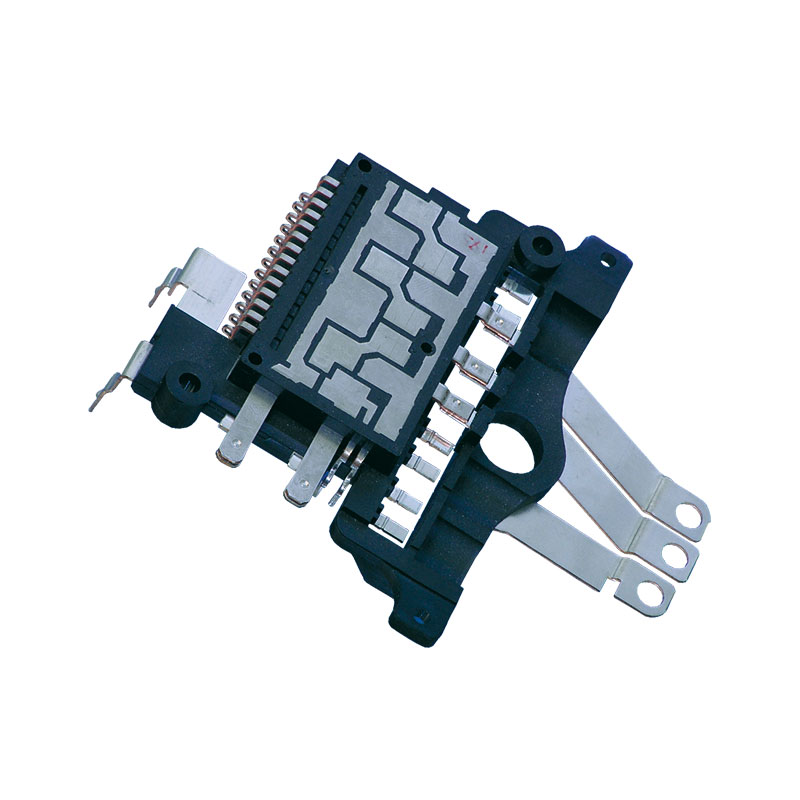
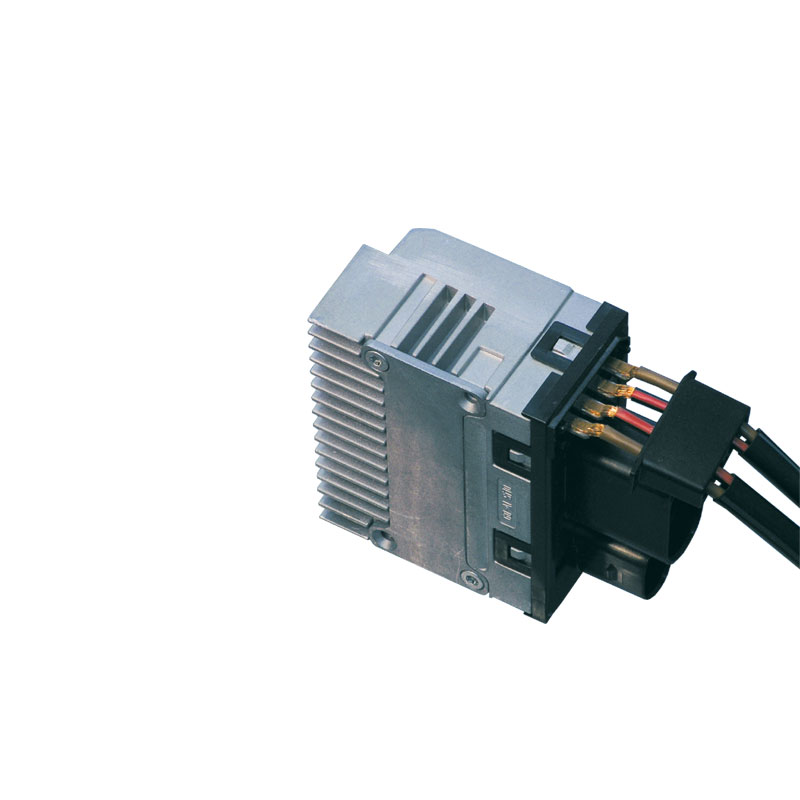
Used in power modules for electric steering systems
Copper strings, tin-plated, to terminals, tin-plated
Used in power modules for electric steering systems
Copper stranded wire to airbag terminal with insulation crimp
Used in power modules for electric steering systems
technologien_terminalschweissen_muster__K_Produkt_Mikro_17
Schweißmodul S-MMD1 zur Buckelschweißung von Stanzteilen zu einem Leadframe
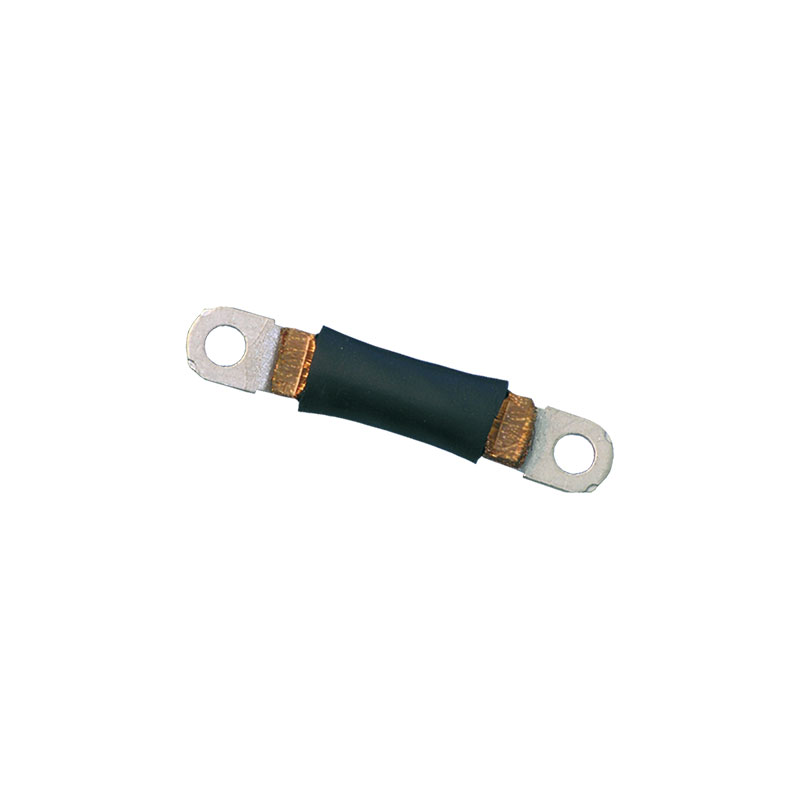
Two-wire sheathed cable with resistor on terminal
Used in power modules for electric steering systems
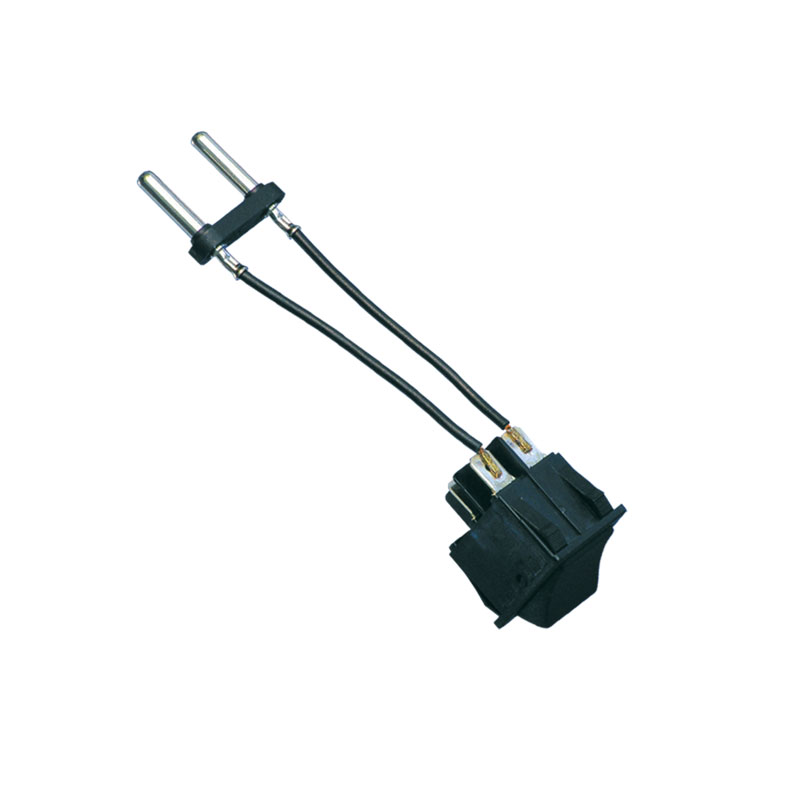
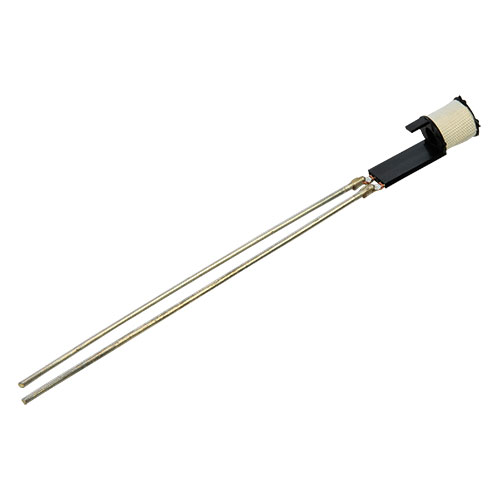
Highly twisted cable sets to magnetic switching system
Used in power modules for electric steering systems
Braid, tin-plated, to copper contact material
Two opposing connection welds of a flat braid to contact material, made with a special seesaw tool
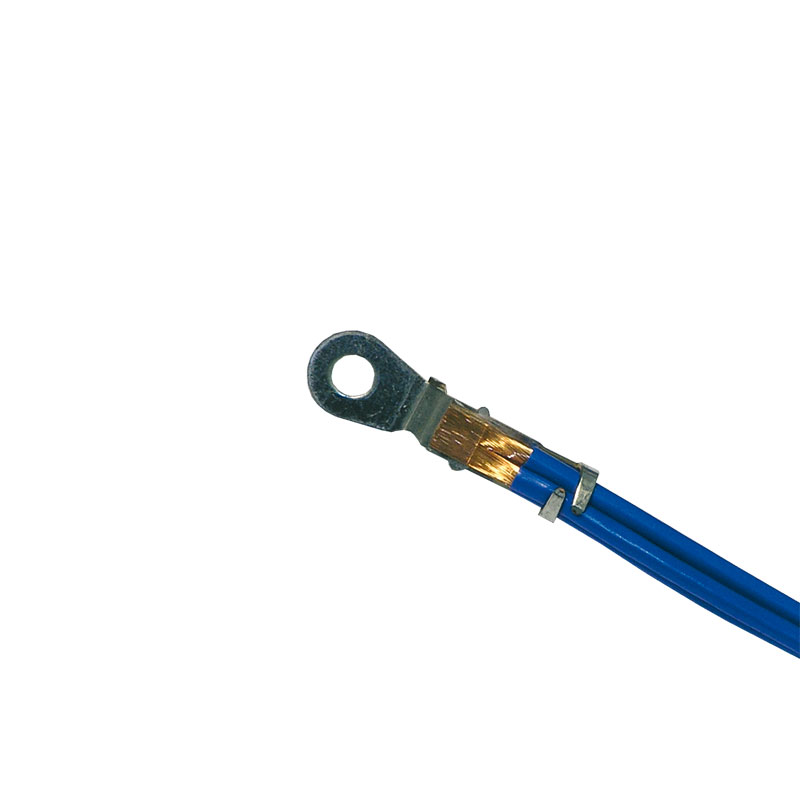
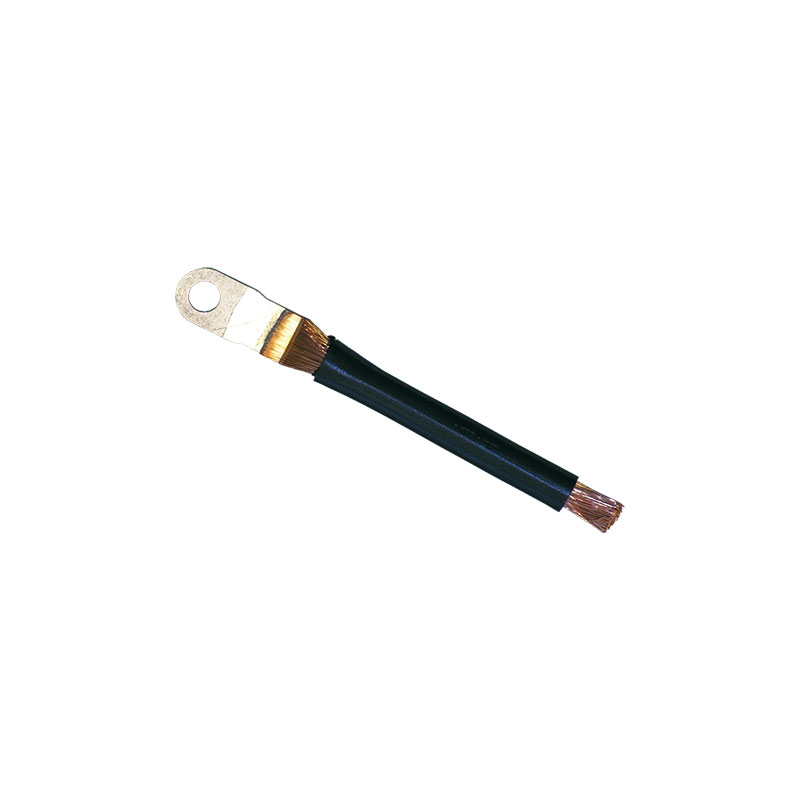
Stranded wires to ground terminal, tin-plated, with insulation crimp
Two opposing connection welds of a flat braid to contact material, made with a special seesaw tool
Stranded wires to ground terminal, tin-plated, with insulation crimp
Two opposing connection welds of a flat braid to contact material, made with a special seesaw tool
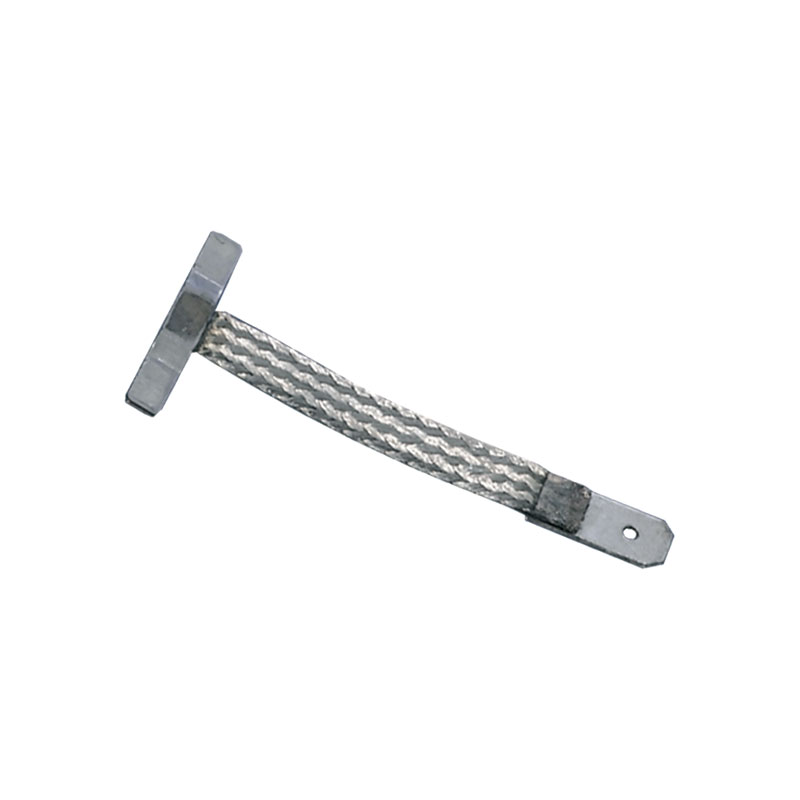
Ground connector with insulation crimp
Two opposing connection welds of a flat braid to contact material, made with a special seesaw tool
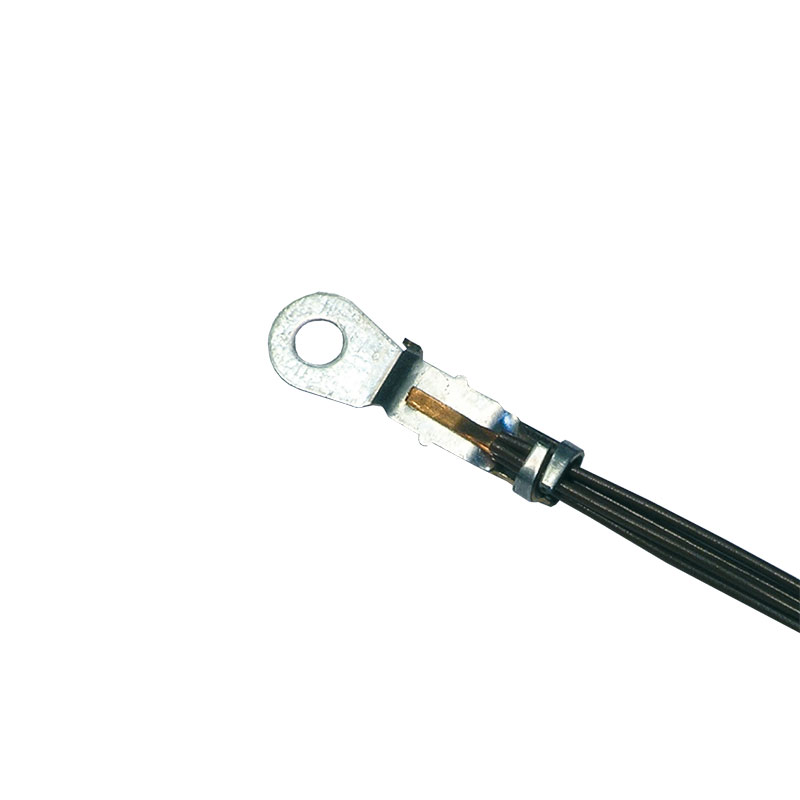
Highly flexible stranded wire to terminal, tin-plated
Two opposing connection welds of a flat braid to contact material, made with a special seesaw tool
Copper strands to current terminal, silver-plated
Two opposing connection welds of a flat braid to contact material, made with a special seesaw tool
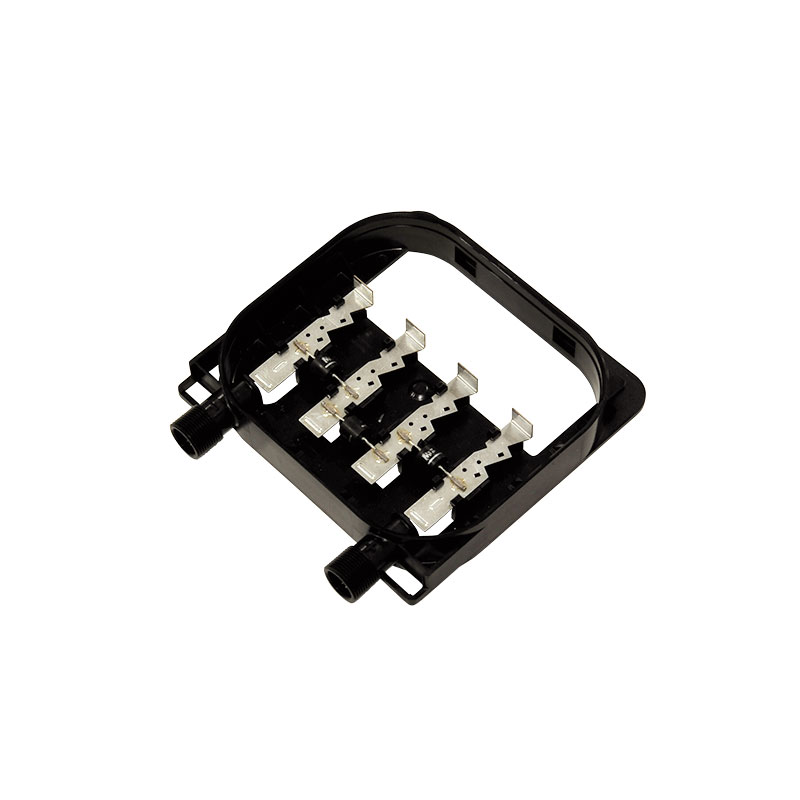
Module connector
Two opposing connection welds of a flat braid to contact material, made with a special seesaw tool
Double cable to busbar
Two opposing connection welds of a flat braid to contact material, made with a special seesaw tool
Module connector
Two opposing connection welds of a flat braid to contact material, made with a special seesaw tool